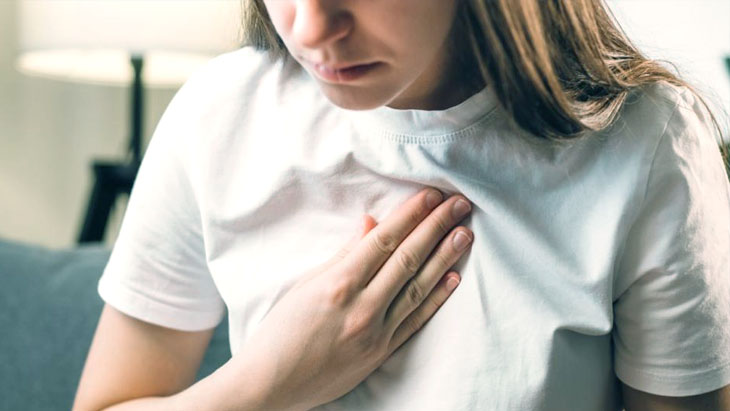
In the realm of cardiovascular and mental health, distinguishing between a heart attack and a panic attack is crucial. The symptoms may overlap, featuring sensations like an accelerated pulse, chest tightness, or shortness of breath. However, understanding that these experiences can stem from two entirely distinct conditions is vital, as they demand different treatment approaches.
Decoding the Heart Attack
During a heart attack, complaints arise from the obstruction of normal blood flow to the heart. In contrast, panic attacks result from the release of stress hormones—cortisol and adrenaline—triggered by a sense of danger.
Overall, the risk of a heart attack is equal for individuals of both genders. Nevertheless, women tend to face this risk at a later age, leading to a less optimistic prognosis.
Gender Dynamics: Heart Attacks vs. Panic Attacks
Conversely, panic attacks and disorders are more prevalent among women than men. Research indicates that the gender gap widens with age. For women aged 15 to 24, the prevalence of panic disorders is 2.5%, compared to 1.3% in men of the same age. While the overall rates decrease in older individuals, the gender gap expands. Among women aged 35 to 44, the frequency of panic disorders was 2.1%, compared to 0.6% in men of the same age.
In addition to higher prevalence rates, women typically suffer from more severe forms of panic disorders.
Distinguishing Between the Two
One of the primary distinctions lies in the development of a heart attack during physical exertion, whereas a panic attack can occur at rest.
Another difference is the duration of complaints. Panic attacks gradually subside and resolve on their own within about 20 minutes, whereas symptoms of a heart attack persist and may worsen over time.
Characteristics of Heart Attack Symptoms:
- Crushing pain and heaviness in the chest
- Sudden onset of complaints during or after physical activity
- Persistent pain in the arm, jaw, or shoulder
- Symptoms worsen over time
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
Typical Complaints in Panic Attacks:
- Rapid or accelerated pulse
- Complaints arise suddenly or during intense stress or anxiety
- Pain that gradually diminishes
- Symptoms resolve within 20–30 minutes
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Numbness in the hands
In the case of a heart attack, immediate medical assistance is paramount. In women, heart attack symptoms may be milder, including unusual fatigue and chest discomfort rather than intense pain. It’s crucial not to underestimate these symptoms, as the condition can deteriorate rapidly.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment of panic attacks depends on their severity. For milder cases, various psychotherapies and relaxation methods such as meditation, acupuncture, yoga, and others may be recommended to alleviate stress.
In conclusion, recognizing the nuanced differences between heart attacks and panic attacks is crucial for prompt and appropriate intervention. Whether it’s a cardiovascular emergency or a manifestation of heightened stress, understanding the unique characteristics of each condition empowers individuals to seek the right care at the right time.